The industrial manufacturing world has amazing ways to turn raw materials into useful and long-lasting products. Aluminum extrusion vs. plastic extrusion are powerful techniques that push material through a die to create uniform cross-sections. While simple in concept, the process yields a remarkable range of applications, from the sleek frames of modern skyscrapers to the ubiquitous plastic bottles we encounter daily.
But when it comes to choosing between aluminum and plastic extrusion, the decision becomes more complex. Both materials boast distinct advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of each process, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications to help you make informed decisions about which material best suits your needs.
Introduction
Extrusion is a process where a material is forced through a precisely shaped die to create a continuous profile with a specific cross-sectional geometry. Imagine squeezing toothpaste through a tube with a special nozzle at the end. That’s essentially how extrusion works.
In the extrusion process, various materials, like plastics, metals, are forced through a mold with a specific shape. This creates long, continuous pieces with the same shape throughout. The type of material used plays a big role in what the final product can be used for. Strong metals like aluminum are extruded to make aircraft parts, while flexible plastics are used for pipes and tubing.
When it comes to shaping materials, aluminum, and plastic extrusion are the two reigning champions, each with its own advantages and limitations. Understanding these nuances is crucial for manufacturers and designers seeking to optimize their products for performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of aluminum and plastic extrusion, exploring their characteristics, applications, and real-world examples.
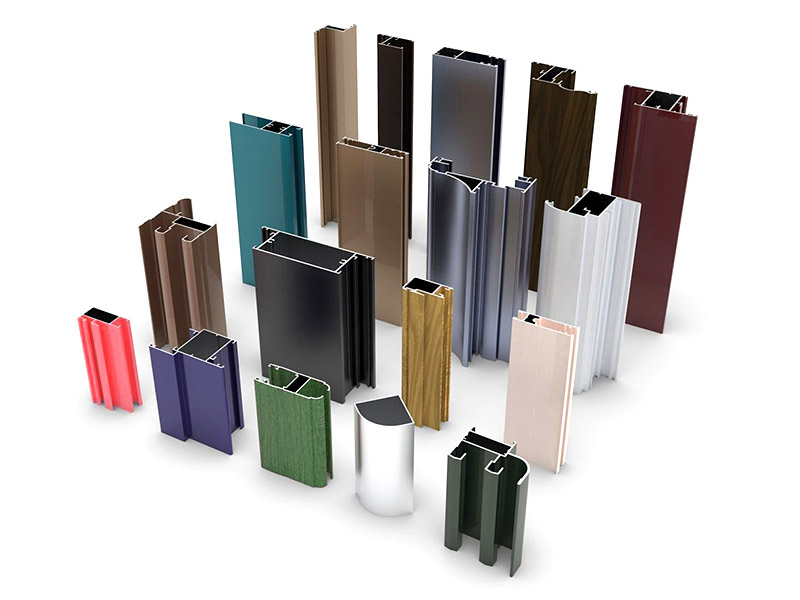

What is Aluminum Extrusion?
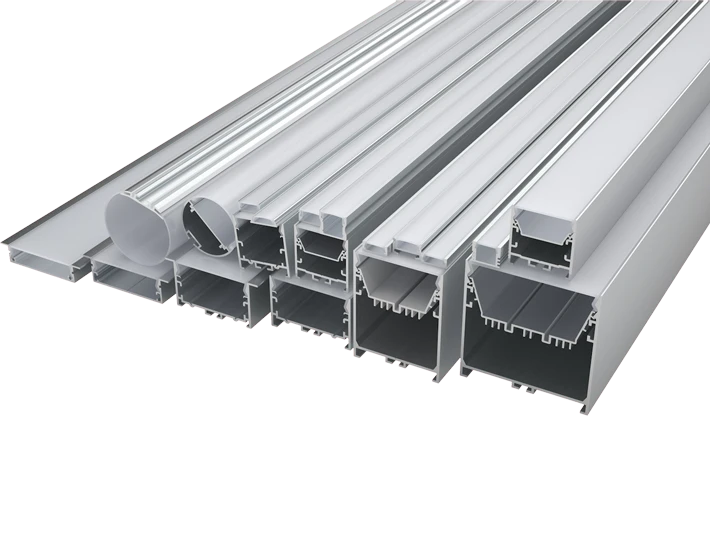
Aluminum extrusion is a widely adopted manufacturing process. In this process, aluminum blocks are heated until they become soft like dough. Then, they’re pushed through a special mold that has the desired shape to form the final aluminum extrusion product. The extruded aluminum profile is long, continuous pieces which are ready for further processing.
Aluminum’s inherent properties make it an ideal choice for extrusion. Its high strength-to-weight ratio, good thermal conductivity, and excellent corrosion resistance contribute to its versatility in many applications.
Aluminum Extrusion Applications
The applications of aluminum extrusion extend across numerous industries. Here are just a few examples:
Construction: Window frames, door frames, cladding panels, curtain walls, structural beams, and architectural profiles.
Automotive: Body panels, engine parts, chassis components, bumpers, and heat sinks.
Aerospace: Aircraft components, satellite parts, rocket bodies, and structural frames.
Consumer goods: Appliances, furniture, electronics, and sporting equipment.
Industrial machinery: Heat exchangers, pipes, and structural components.
Specific examples include:
Window frames: Aluminum extrusion creates durable, energy-efficient window frames that resist corrosion and offer superior thermal insulation.
Aircraft components: Aluminum extrusion is essential in aerospace due to its lightweight and high-strength properties, making it suitable for structural components like spars and ribs.
Heat sinks: Aluminum’s excellent thermal conductivity makes it ideal for heat sinks, which dissipate heat generated by electronic components.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum Extrusion
Advantages:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: When it comes to materials that are strong yet lightweight, aluminum stands out as the undisputed champion. This unique combination of strength and low weight makes aluminum the ideal choice for applications where weight is a major concern, such as in aircraft, automobiles, and lightweight construction materials.
Exceptional Durability: Aluminum’s inherent strength makes it highly resistant to wear, tear, and corrosion. This remarkable resilience ensures that aluminum products can withstand the test of time, even in harsh environments.
Resilience Against Corrosion: Aluminum forms a protective oxide layer that shields it from the ravages of corrosion. This protective shield makes aluminum a dependable choice for outdoor applications, like window frames, siding, and bridges.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum is an excellent conductor of both heat and electricity. This makes it a go-to material for heat sinks, electrical wiring, and components that need to efficiently manage heat or electricity.
Recyclable and Sustainable: Aluminum is infinitely recyclable, meaning it can be melted down and reused without losing its properties. This eco-friendly nature makes aluminum a sustainable choice for responsible manufacturers and consumers.
Disadvantages:
Limited Design Flexibility: While aluminum can be extruded into complex shapes, its inherent rigidity might limit design flexibility compared to plastic extrusion.
Higher Cost: Aluminum extrusion often comes with a higher price tag compared to plastic extrusion. This is mainly due to the cost of raw aluminum materials and the specialized equipment required for the process.
Specialized Tooling and Equipment: The precision and complexity of aluminum extrusion require specialized tooling and equipment, which can add to the initial investment cost.
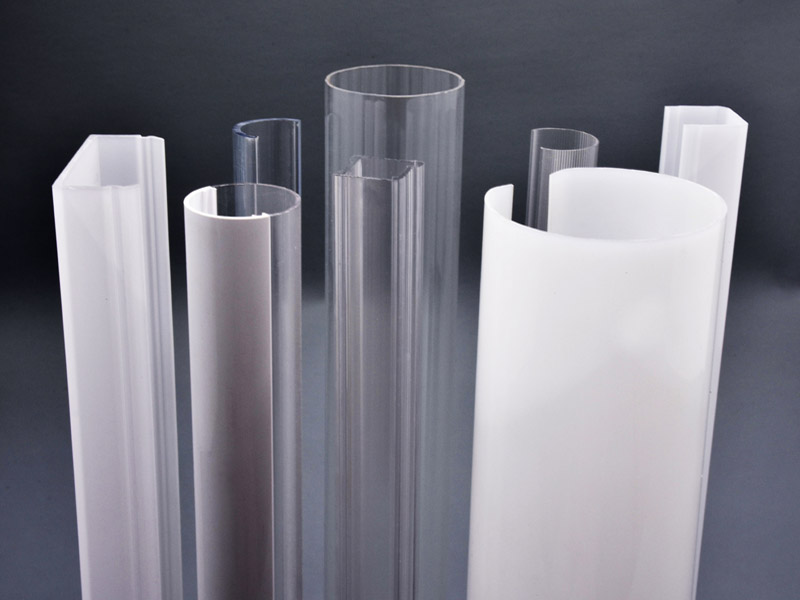

What is Plastic Extrusion?
Similar to aluminum extrusion, plastic extrusion is a manufacturing process that transforms raw plastic materials into various shapes and forms. This versatile technique involves feeding thermoplastic polymers into a heated mold called a die. The die’s unique shape dictates the final profile of the extruded plastic.
The plastic extrusion process begins with melting the plastic pellets or granules. This molten plastic is then forced through the die opening, taking on the die’s shape. And then cooling it down to solidify the extruded profile.
Plastic extrusion stands out for its remarkable flexibility and adaptability. Thermoplastics, the materials used in this process, exhibit a wide range of properties, allowing manufacturers to create products with diverse characteristics. Plastic extrusion can deliver whatever you need flexible tubing, rigid pipes, or even transparent sheets.
Plastic Extrusion Applications
Plastic extrusion finds application in a vast array of industries, producing a multitude of products, including packing:
Packaging: Bottles, containers, films, tubes, and packaging films.
Automotive: Interior parts, trims, dashboard components, and exterior cladding.
Medical devices: Tubing, syringes, catheters, and disposable medical components.
Consumer products: Toys, furniture, appliances, and household goods.
Construction: Pipes, window frames, door frames, and siding.
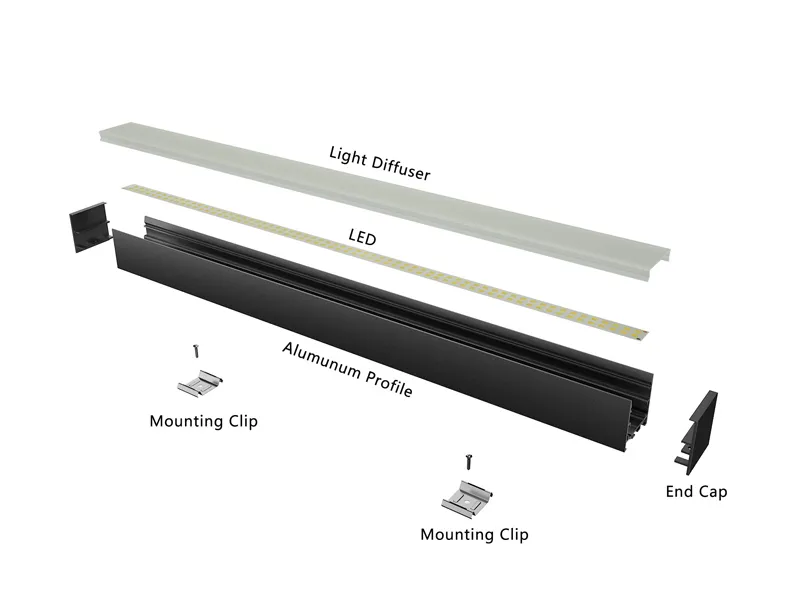
Lighting: plastic led profiles, light diffusers, lens
Specific examples include:
Plastic bottles: PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is commonly used in plastic extrusion for producing bottles due to its lightweight, recyclable nature, and resistance to chemicals.
Automotive interior parts: Polypropylene and PVC (polyvinyl chloride) are often used in automotive interiors due to their flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals.
Medical tubing: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethylene are widely used in medical tubing due to their biocompatibility and ease of sterilization.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastic Extrusion
Advantages:
Lower Cost: Plastic extrusion typically costs less than aluminum extrusion, making it an attractive choice for budget-conscious projects. This cost advantage is driven by the affordability of plastic raw materials and simpler processing equipment.
Design Flexibility: Plastic extrusion shines in terms of design flexibility. It allows for the creation of complex shapes, intricate patterns, and customized profiles that are difficult to achieve with aluminum.
Lightweight and Easy to Handle: Plastic extrusions are generally lightweight, making them easy to handle, transport, and assemble. This attribute is particularly valuable in applications where weight is a critical factor.
A Rainbow of Colors and Finishes: Plastic offers a vast array of colors, textures, and finishes, allowing for customization and aesthetic appeal. This diversity caters to design preferences and branding needs.
Disadvantages:
Lower Strength and Durability: While some plastics are strong, they generally lack the strength and durability of aluminum. This limitation means that plastic extrusions might not be suitable for applications demanding high load-bearing capacity or long-term resilience.
Sensitivity to heat and UV degradation: Some plastics degrade when exposed to high temperatures or prolonged UV radiation. This degradation can lead to brittleness, discoloration, or loss of structural integrity.
Limited thermal and electrical conductivity: Most plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity, making them unsuitable for applications in thermal management or electrical components.
Environmental concerns: While some plastics are recyclable, the environmental impact of plastic production and disposal is growing increasingly concerning. The choice of plastic type and responsible disposal practices are crucial to minimize the environmental footprint.
Aluminum Extrusion vs. Plastic Extrusion: A Detailed Comparison
To help you choose between aluminum and plastic extrusion, let’s take a closer look at each process and compare their pros and cons:
Material properties
| Aluminum: | Plastics: |
| Strength: High | Strength: Varies |
| Durability: High | Durability: High |
| Weight: Lightweight | Weight: Lightweight |
| Thermal Conductivity: Excellent | Thermal Conductivity: Poor |
| Cost: Relatively high | Cost: Relatively high |
| Environmental Impact: Recyclable, but production is energy-intensive | Environmental Impact: Recyclable, some difficult or impossible |
Manufacturing Process
Both aluminum and plastic extrusion share similarities in their manufacturing processes: heating the material to a malleable state and forcing it through a die. However, some key differences exist:
Temperature: Aluminum requires significantly higher temperatures than plastic to become malleable.
Die materials: Aluminum extrusion often utilizes hardened steel dies, while plastic extrusion can employ dies made of various materials, including steel, brass, and bronze.
Cooling: Aluminum extrusion process often involves cooling the extruded profile with water or air to maintain its shape, while plastic extrusion typically relies on air cooling.
Applications
The choice between aluminum and plastic extrusion largely depends on the specific application and its requirements.
Aluminum extrusion is ideal for applications demanding high strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Examples include structural components in aerospace, construction, and automotive industries.
Plastic extrusion is suitable for applications where cost-effectiveness, lightweight construction, and design flexibility are paramount. Examples include packaging, consumer products, and automotive interior components.
Choose the Right Extrusion Material
Selecting the appropriate extrusion material is crucial for ensuring the success of any project. To make an informed decision, these factors should be carefully considered.
Project requirements: What are the primary functional needs of the product? Strength, durability, weight, and cost are key considerations.
Application environment: Will the product be exposed to extreme temperatures, humidity, chemicals, or UV radiation? The environment in which the product will operate dictates the material’s suitability.
Desired aesthetic appeal: Does the product require a specific color, finish, or texture? Both aluminum and plastic offer various aesthetic options, allowing you to achieve the desired visual appeal.
Sustainability and recyclability: Are environmental considerations important for the product? Aluminum is highly recyclable, while the recyclability of plastics varies greatly depending on the type of resin used.
Real-World Examples
To illustrate the practical implications of choosing between aluminum and plastic extrusion, let’s consider some real-world examples:
Window frames: Aluminum extrusion is a popular choice for window frames due to its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. While plastic windows can be more cost-effective, they may not offer the same level of longevity and thermal performance.
Bottles: PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is commonly used in plastic extrusion for producing bottles, while aluminum is less common due to its higher cost and less malleability. However, aluminum bottles are becoming increasingly popular due to their sustainability and recyclability.
Automotive interior parts: Plastic extrusion is extensively used for automotive interior parts like dashboards, door panels, and trims. Aluminum is less common in these applications due to its higher cost and potential for corrosion.
Aircraft components: Aluminum extrusion is critical in aerospace due to its lightweight, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for structural components like spars, ribs, and skins. Plastic is rarely used in these applications due to its limited strength and durability.
Conclusion
The choice between aluminum and plastic extrusion will finally be determined when you have a better understanding of your specific application and its requirements. While both materials offer unique advantages and disadvantages, carefully considering factors like strength, durability, cost, and environmental impact will guide you toward the optimal choice.
Remember that aluminum extrusion is ideal for applications demanding high strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, while plastic extrusion shines in applications requiring cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and lightweight construction. When multiple factors need to be considered for complex applications, you should seek advice from experienced manufacturers and engineers.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the world of aluminum and plastic extrusion. We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions with us in the comments section or by email. If you have any projects involving aluminum profile extrusion or plastic extrusion, feel free to ask for assistance from us.